March 13, 2020 -- The weak link in the U.S. response to diagnostic testing for the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 could be a shortage of RNA extraction kits. Fortunately, suppliers of RNA purification kits are working overtime to get more kits into circulation.
Politico reported on March 10 that Dr. Robert Redfield, director of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), said on Tuesday that he is not confident that U.S. labs have an adequate stock of the supplies used to extract genetic material from any virus in a patient's sample -- a critical step in coronavirus testing.
The article goes on to quote Dr. Michael Mina, PhD, assistant professor of epidemiology at the Harvard University T.H. Chan School of Public Health, as saying, "RNA extraction is the first step in being able to perform" a coronavirus test. "If we cannot perform this step, the [coronavirus] test cannot be performed."
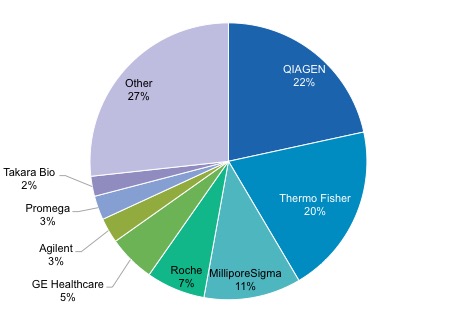
Qiagen was cited as a major supplier of RNA purification kits, but these are on backorder due to worldwide demand for coronavirus testing. While we know from our own analysis of the market that Qiagen is indeed a major player in the market, there are certainly many other options for labs to turn to.
First, a little background. Nucleic acid (NA) sample preparation can be defined as any operation starting with a biological sample and ending in analysis of nucleic acid, namely DNA and/or RNA, that is carried out in a given workflow. This sample preparation step is critical for multiple reasons, including prevention of nucleic acid degradation and minimizing contamination.
Current methods for nucleic acid isolation include column-based purification and biomagnetic separation. Both methods take advantage of the affinity of silica for nucleic acid materials; column-based methods involve binding NA materials to silica membranes contained in plastic columns, while biomagnetic separation utilizes silica-coated magnetic beads.
Since RNA differs structurally from DNA (the former being single-stranded, while the latter is double-stranded), the pH and salt concentration of the binding solution can be optimized for binding of one or the other. In this way, RNA preparation kits specifically target RNA molecules for isolation.
For RNA purification using columns, cells are first lysed to release nucleic acid contents, and the lysate mixture, containing RNA binding buffers, is passed through the column. RNA remains bound in the column while other materials are washed away. Elution yields purified RNA.
When done manually, liquids are forced through the columns by centrifugation. Alternatively, a vacuum manifold can be used to draw liquids through. Automated column extraction incorporates liquid handling robots and vacuum manifolds, allowing high-throughput preparation of RNA samples.
Biomagnetic separation technology is a more recently developed method for nucleic acid purification. The process, which is gentler than other methods, involves moving the liquid sample through silica-coated beads, much like liquid chromatography.
By agitation, a suspension of these magnetic beads is thoroughly mixed with a lysate mixture containing the RNA and binding buffer. A magnet is then used to immobilize the magnetic particles and trap the RNA, while the unbound materials are removed by aspiration. The bound RNA molecules are detached from the beads, washed, and collected for subsequent analysis or further manipulation.
Biomagnetic bead separation offers several advantages in that it subjects the analytes to very little mechanical stress, produces higher purity, and can increase product yields. This makes biomagnetic separation more suitable when isolating longer targets or if secondary or even tertiary structures need to be preserved.
The suppliers of RNA purification kits are numerous and include both large and small companies.
RNA kit suppliers
- abm
- Abnova Corporation
- Agilent (Stratagene)
- Analytik Jena
- Apical
- AS One International
- Corning Life Sciences (Axygen)
- Biotium
- Beckman Coulter
- Bio-Rad
- Biobasic
- BioChain
- Biorbyt
- Biotium
- BioVision
- BosterBio
- Civic Bioscience
- Enzo Life Sciences
- EpiGentek
- EZ Bioresearch
- G Biosciences
- GE Healthcare Life Sciences
- Genaxxon Biosciences
- Genesig
- Jena Bioscience
- Lexogen
- LifeSpan BioSciences
- Lucigen
- Macherey Nagel
- MilliporeSigma
- Minerva Biolabs
- MyBioSource.com
- New England Biolabs
- Norgen Biotek
- Omega BioTek
- PerkinElmer
- Promega
- Rx Biosciences
- TaKaRa (Clontech)
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- TransGen Biotech
- Zageno
- Zymo Research
Let's hope these firms can move quickly to help meet the growing demand.
Alice Kan is a senior market analyst at Strategic Directions International (SDi), the leading business intelligence firm in the highly specialized field of analytical and life science instruments.
Disclosure: The Science Advisory Board is a sister company of SDi.
Copyright © 2020 scienceboard.net






