 mRNA vaccines are successful for COVID-19. But what about cancer?
mRNA vaccines are successful for COVID-19. But what about cancer?
Advances in platform technology for the development of messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccines have led to the authorization of several COVID-19 vaccines. But scientists are also working on developing mRNA vaccines to protect against or treat other diseases, such as cancer. This includes a hydrogel-based RNA vaccine, the design of which is discussed in an article published in Nano Letters on February 1. Read More
 Proteomics helps researchers pick the best anti-SARS-CoV-2 nanobodies
Proteomics helps researchers pick the best anti-SARS-CoV-2 nanobodies
A new high-throughput proteomics-based strategy to identify tiny antibody fragments -- called nanobodies -- may provide an efficient and effective method for developing therapeutics against the deadly SARS-CoV-2 virus -- including variants. The findings were published in Cell Systems on February 15. Read More
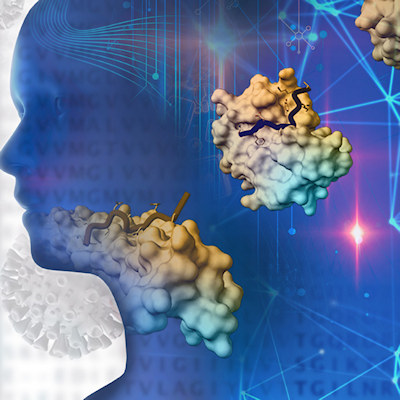 Scientists identify missing molecular links to SARS-CoV-2, host interactions
Scientists identify missing molecular links to SARS-CoV-2, host interactions
Researchers have identified interactions between short viral proteins and receptors that facilitate the entry of the SARS-CoV-2 virus into a host. This evidence of molecular links, published in Science Signaling on February 12, may help scientists identify drugs that are highly effective at blocking the virus. Read More
 Benchtop capillary electrophoresis opens new doors for sample identification
Benchtop capillary electrophoresis opens new doors for sample identification
Sample identification and verification is essential to research that interrogates and compares specific regions of the human genome, called short tandem repeats. Benchtop capillary electrophoresis is a sample identification method that can be easily implemented in research labs for many forensic and research applications. Read More
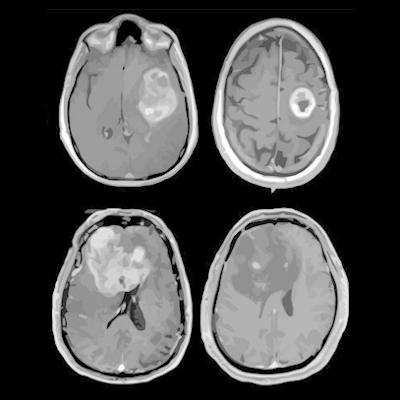 Multiomics approach profiles molecular characteristics of glioblastoma
Multiomics approach profiles molecular characteristics of glioblastoma
A team of more than 40 investigators has created a profile of the genes, proteins, infiltrating cells, and signaling pathways of the deadly brain cancer glioblastoma. The findings could lead to better patient care, according to the authors of a new study published February 11 in Cancer Cell. Read More
 Researchers use modified CRISPR tool to manipulate the epigenome
Researchers use modified CRISPR tool to manipulate the epigenome
Bioengineers have developed a new way to engineer the human epigenome (chemical changes in the DNA) using a modified CRISPR-Cas9 system to target and activate proteins in the chromosome. This research, published in Nature Communications on February 9, expands on synthetic genome tools. Read More
 NIH adds long-acting antibody COVID-19 therapy to ACTIV-3 master protocol
NIH adds long-acting antibody COVID-19 therapy to ACTIV-3 master protocol
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) has begun a new arm of its master protocol, the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines 3 (ACTIV-3) study, which evaluates the safety and efficacy of an investigational long-acting antibody combination for the treatment of patients hospitalized with COVID-19. Read More
 COVID-19 vaccines may be causing orofacial reactions
COVID-19 vaccines may be causing orofacial reactions
The two COVID-19 vaccines being given to patients in the U.S. and other countries have been linked to orofacial adverse drug reactions such as temporary facial paralysis, according to a brief report published on February 1 in the Journal of Oral Pathology & Medicine. Read More
 New synthetic biology approach may improve delivery of programmable medicines
New synthetic biology approach may improve delivery of programmable medicines
Programmable medicines that can be controlled by synthetic genetic components are not yet a clinical reality. But synthetic components can now be reconfigured so they don't overwhelm host cells, moving the technology a step closer to clinical reality, according to new research published February 8 in Nature Communications. Read More
 Deep-learning approach points the way to faster COVID-19 vaccines
Deep-learning approach points the way to faster COVID-19 vaccines
A novel deep neural network can target the most promising multiepitope COVID-19 vaccine candidates in a matter of seconds. The new artificial intelligence framework, which was described in Scientific Reports on February 5, may give scientists an edge in the race against SARS-CoV-2 and its variants by reducing the time from vaccine design to clinical trials. Read More
Member Rewards
Earn points for contributing to market research. Redeem your points for merchandise, travel, or even to help your favorite charity.
Research Topics
Interact with an engaged, global community of your peers who come together to discuss their work and opportunities.
Connect
Tweets by @ScienceBoard



