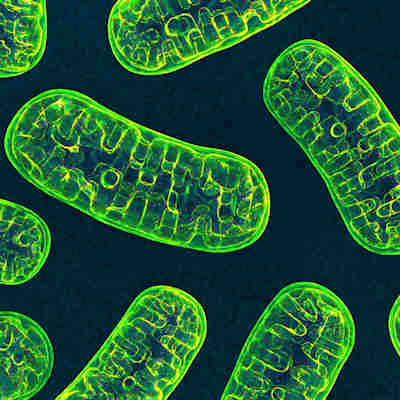
September 29, 2022 -- The shape and function of the immune system’s Th17 mitochondria play a key role in autoimmune and inflammatory disorders such as multiple sclerosis, new research suggests.
Scientists from the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center in Baltimore identified several avenues for trying to influence T-cell behavior with the goal of diminishing their autoimmune activity. In their study, among three main T effector cell types, only Th17 cells had elongated mitochondria, which is strange because elongated mitochondria are usually seen in resting cells and not in activated cells, the authors said (Nature, September 28, 2022).
They knew the OPA1 gene regulates mitochondrial fusion, but what happens when the gene is deleted? The mitochondria reverted to a more fragmented size and shape. However, the cells also stopped producing the signaling molecule interleukin-17 (IL-17). In animal studies, deleting the OPA1 gene stopped IL-17 production and abated disease symptoms.
However, OPA1 deletion did not affect energy production and a central biochemical process occurring in the mitochondria was altered, causing buildup of a metabolite known to influence DNA and the cell's transcriptional program. The molecule dampened the ability of the cell to read its DNA, and consequently, IL-17 was no longer produced, they found.
In cells missing OPA1, the researchers discovered a large increase in the activated form of the protein LKB1, a metabolic sensor that regulates cellular metabolism, cell division, and mitochondrial function. When both OPA1 and LKB1 were deleted, IL-17 production was restored and the mitochondrial processes returned to normal.
Copyright © 2022 scienceboard.net