 NCI awards $4.2M to Mount Sinai to create Proteogenomic Data Analysis Center
NCI awards $4.2M to Mount Sinai to create Proteogenomic Data Analysis Center
The National Cancer Institute (NCI) has awarded $4.2 million over five years to Mount Sinai researchers to establish a Proteogenomic Data Analysis Center to advance cancer research and treatments. Read More
 New stem cell mechanism in mice intestines has potential human application
New stem cell mechanism in mice intestines has potential human application
Researchers have found a new biophysical mechanism that regulates stem cells in the intestines of mice, which could have implications for potential new treatments for human diseases. Read More
 Researchers target protein to hasten search for next COVID-19 antiviral
Researchers target protein to hasten search for next COVID-19 antiviral
A new approach to identifying molecules that interfere with the protein nsp13 could speed up the search for the next COVID-19 antiviral and lead to development of pan-coronavirus antivirals. Read More
 Study finds cancer cells gravitate toward mechanical ‘sweet spot’ environments
Study finds cancer cells gravitate toward mechanical ‘sweet spot’ environments
An international team of researchers, led by University of Minnesota Twin Cities engineers, has discovered that cancer cells invade the body based on the stiffness of their environment, providing a new understanding of how cancer spreads and the potential for improvements to future treatments. Read More
 Researchers determine first cryo-EM full-length structures of ACE
Researchers determine first cryo-EM full-length structures of ACE
Using cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), researchers from the University of Cape Town have determined the first full-length structures of the human angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), a blood pressure-regulating protein, which they say could help improve drug design for heart disease. Read More
 Bio-Rad extends range of anti-idiotypic antibodies for bioanalysis, drug monitoring
Bio-Rad extends range of anti-idiotypic antibodies for bioanalysis, drug monitoring
Bio-Rad Laboratories has extended its range of recombinant monoclonal anti-idiotypic antibodies with the introduction of antibodies specific to brentuximab vedotin, secukinumab, and the secukinumab-interleukin 17A drug-target complex. Read More
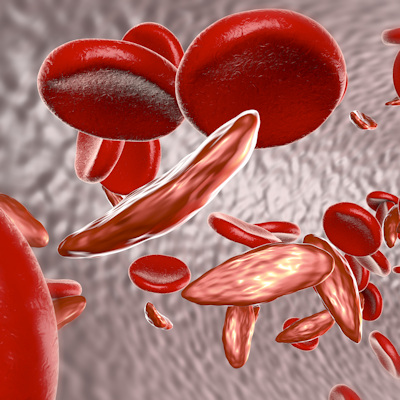 Researchers identify which mice not to use for sickle cell disease studies
Researchers identify which mice not to use for sickle cell disease studies
Researchers in Memphis, TN, have learned why certain mice die when testing new gene-based therapies for sickle cell disease and encourage scientists to carefully consider the genetics of the mice they are using to study human diseases. Read More
 Scientists discover why sound blunts pain in mice
Scientists discover why sound blunts pain in mice
An international team of researchers have discovered exactly why sound can reduce pain, at least in mice. Read More
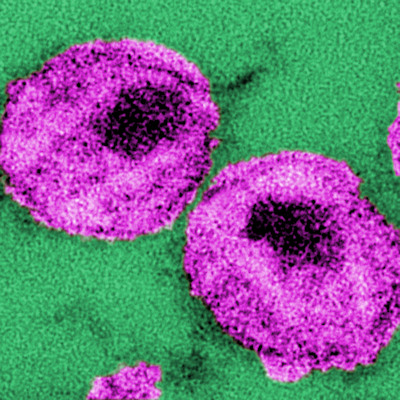 2-step molecular strategy spots HIV-1
2-step molecular strategy spots HIV-1
Scripps Research scientists and collaborators have discovered the innate immune system uses a two-step molecular strategy to detect HIV-1, even when the virus is present in very small amounts. Read More
 Researchers develop 'wise counsel' for biological systems
Researchers develop 'wise counsel' for biological systems
Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Terrestrial Microbiology created Machine Learning Guided Experimental Trials for Improvement of Systems, a modular software system for optimizing biological systems. Read More
Member Rewards
Earn points for contributing to market research. Redeem your points for merchandise, travel, or even to help your favorite charity.
Research Topics
Interact with an engaged, global community of your peers who come together to discuss their work and opportunities.
Connect
Tweets by @ScienceBoard



