 Researchers develop mouse model of COVID-19 infection
Researchers develop mouse model of COVID-19 infection
Researchers have generated a strain of SARS-CoV-2 that can infect mice and used it to produce a new mouse model of infection to help facilitate testing of COVID-19 vaccine candidates and therapies. The research article was published in Science on July 30. Read More
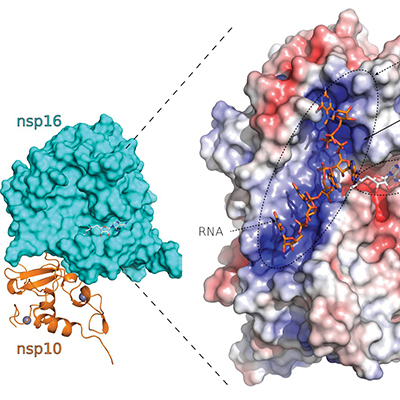 Researchers further define nonstructural protein targets of SARS-CoV-2
Researchers further define nonstructural protein targets of SARS-CoV-2
The crystal structure of nonstructural protein 16 of SARS-CoV-2, which plays a role in viral RNA capping to mimic host messenger RNA, reveals specific rational design targets that could be used to develop effective therapies against SARS-CoV-2 and other coronaviruses. The research was published in Nature Communications on July 24. Read More
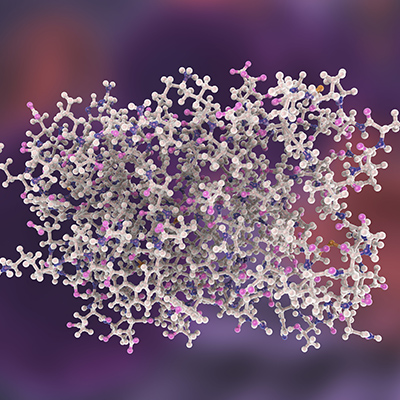 Inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease may stop viral spread
Inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease may stop viral spread
Another nonstructural protein, papain-like protease, has been identified as a SARS-CoV-2 therapeutic target with the potential to block viral replication, according to an article published in Nature on July 29. Read More
 Human-infecting coronaviruses have lived in bats for decades
Human-infecting coronaviruses have lived in bats for decades
Genome sequencing of the SARS-CoV-2 virus has revealed that the type of virus family to which the novel coronavirus belongs most likely first emerged in bats in the late 1960s, according to a new study published in Nature Microbiology on July 28. Read More
 Animal study turns in positive results for Moderna-NIH COVID-19 vaccine
Animal study turns in positive results for Moderna-NIH COVID-19 vaccine
Moderna's COVID-19 vaccine candidate, messenger RNA (mRNA)-1273, has been shown to induce immune responses and control upper and lower respiratory tract infection of rhesus macaques exposed to SARS-CoV-2, according to researchers from the U.S. National Institutes of Health's (NIH) National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Read More
 Genetic regulation of immune diseases starts at birth
Genetic regulation of immune diseases starts at birth
Areas of the human genome may explain the early origins of chronic immune and inflammatory diseases that develop later in life, according to a study published in Nature Communications on July 28. Read More
 Imaging finds tooth decay's root, may lead to ways to fight it
Imaging finds tooth decay's root, may lead to ways to fight it
Atom probe tomography and other techniques revealed that human enamel contains small chemical flaws that may affect the resiliency of the fundamental building blocks of teeth, in a study published July 2 in Nature. Read More
 SARS-CoV-2 envelope protein identified as target for antiviral drugs
SARS-CoV-2 envelope protein identified as target for antiviral drugs
Comparison of the SARS-CoV-2 genome with other betacoronaviruses can provide useful information on how drugs targeting other coronaviruses may improve outcomes for COVID-19 patients. The analysis was presented in a July 27 Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology article. Read More
 SARS-CoV-2 disguises its own genetic material to facilitate infection
SARS-CoV-2 disguises its own genetic material to facilitate infection
The SARS-CoV-2 virus is able to camouflage itself to promote viral replication, as revealed by structural details of proteins on the surface of the virus. Researchers discovered an enzyme that they believe could be an important target for antiviral drug development, according to a July 14 Nature Communications report. Read More
 New tools rapidly detect anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies
New tools rapidly detect anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies
New tools using surrogate viruses may be useful for rapid testing to determine whether antibodies effectively neutralize SARS-CoV-2. The viral vector-based platform approach was published in the Journal of Experimental Medicine on July 21. Read More
Member Rewards
Earn points for contributing to market research. Redeem your points for merchandise, travel, or even to help your favorite charity.
Research Topics
Interact with an engaged, global community of your peers who come together to discuss their work and opportunities.
Connect
Tweets by @ScienceBoard



