September 10, 2020 -- Curi Bio released its new proprietary ComboMat platform, a human induced pluripotent stem cell cardiomyocyte (hiPSC-CM) maturation technology with applications in drug discovery, disease modeling, and safety and efficacy screening.
ComboMat leverages a proprietary microRNA cocktail to drive the functional development and maturation of cardiomyocytes. The platform will be available to pharmaceutical customers through service contracts and partnerships. The product was developed to recapitulate some aspects of human toxicity in vitro, a leading cause of drug candidate failure in clinical trials.
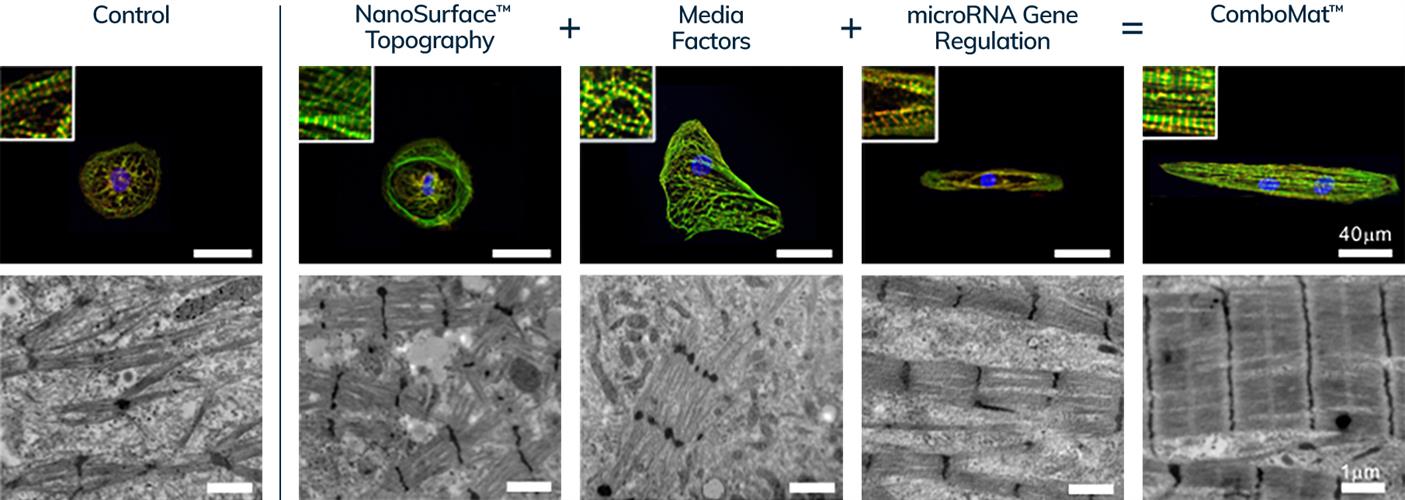
ComboMat is a combinatorial maturation platform that uses NanoSurface technology, media factors, and a gene expression-regulating mircoRNA cocktail to synergistically advance the maturation of hiPSC-derived cardiomyocytes. ComboMat-treated cells exhibit enhanced structural, electrophysiological, contractile, and metabolic development, resulting in more human, adult-like cell models for better utility during drug development, according to the firm.
The cardiomyocytes derived from the platform can create high-fidelity models of human disease and can also be used to create stratified hiPSC-CM-based disease models including Duchenne muscular dystrophy associated cardiomyopathy and other metabolic diseases.
Curi's ComboMat platform integrates proprietary methods and intellectual property exclusively licensed to Curi Bio by the University of Washington.
Copyright © 2020 scienceboard.net