 Future Fields, Jenthera Therapeutics collaborate to develop novel protein for the delivery of cancer biologics
Future Fields, Jenthera Therapeutics collaborate to develop novel protein for the delivery of cancer biologics
June 15, 2023 -- Biotech firm Future Fields and gene-editing firm Jenthera Therapeutics this week announced a collaboration focused on the manufacturing of a first-of-its-kind cancer-fighting protein. Read More
 Conductive, jelly-like material opens door to safer, more durable medical implants
Conductive, jelly-like material opens door to safer, more durable medical implants
June 15, 2023 -- Engineers have developed a jelly-like material that conducts electricity for use as an alternative to metal electrodes in medical implants. Read More
 Stem cell-derived islet cell therapy shows promise for individuals with type 1 diabetes
Stem cell-derived islet cell therapy shows promise for individuals with type 1 diabetes
June 26, 2023 -- An ongoing clinical trial for patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D) demonstrated the potential of stem cell-derived islet cell therapy, called VX-880, as a future treatment option for patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D), the American Diabetes Association (ADA) said on Friday. Read More
 Rare disease discovered after scientists probe cause of inflammatory symptoms
Rare disease discovered after scientists probe cause of inflammatory symptoms
June 22, 2023 -- Researchers have discovered a rare disease by running genetic, immunologic, and molecular assays in four patients. Read More
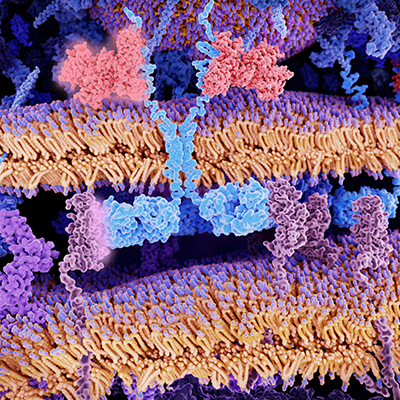 Resistant leukemia treated with base-edited T cells
Resistant leukemia treated with base-edited T cells
June 15, 2023 -- Three young patients with relapsed T-cell leukemia have now been treated with base-edited T cells, in an ongoing clinical trial collaboratively conducted by University College London (UCL) and Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children (GOSH). Read More
 BioCentriq, Kytopen expand partnership on cell therapy manufacturing technology
BioCentriq, Kytopen expand partnership on cell therapy manufacturing technology
June 6, 2023 -- BioCentriq, a contract development and manufacturing organization specializing in cell therapy, and Kytopen, a Massachusetts Institute of Technology-based startup, on Tuesday announced that they are expanding their partnership. Read More
 Bio-Techne to acquire Swiss spatial biology firm Lunaphore
Bio-Techne to acquire Swiss spatial biology firm Lunaphore
June 22, 2023 -- Bio-Techne announced Thursday that it has reached an agreement to acquire Tolochenaz, Switzerland-based Lunaphore, a developer of fully automated spatial biology products. Read More
 Imaging technique for biological samples combines best of current methods
Imaging technique for biological samples combines best of current methods
June 16, 2023 -- Researchers have developed an imaging technique that combines the best attributes of two current ways of viewing biological samples on a microscopic level. Read More
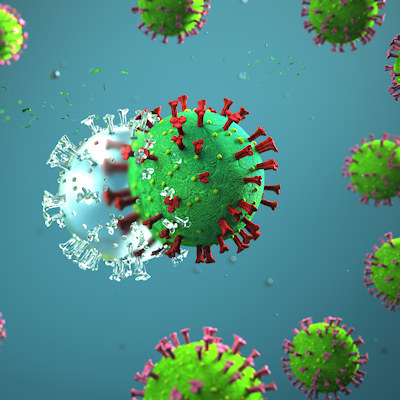 Taking metformin during SARS-CoV-2 infection cuts risk of long COVID in clinical trial
Taking metformin during SARS-CoV-2 infection cuts risk of long COVID in clinical trial
June 9, 2023 -- People who took the diabetes drug metformin after being infected with SARS-CoV-2 were less likely to develop long COVID in a randomized clinical trial. Read More
 Quantification of long COVID fatigue shows impact is worse than some cancers
Quantification of long COVID fatigue shows impact is worse than some cancers
June 7, 2023 -- Fatigue is the most impactful symptom in the lives of people suffering from long COVID, with patients reporting worse scores than individuals with some cancers. Read More
 Genomics AI firm Genomenon acquires Boston Genetics
Genomics AI firm Genomenon acquires Boston Genetics
June 27, 2023 -- Genomenon on Tuesday said that it has acquired the genomics interpretation and curation firm Boston Genetics. Read More
 Asep gets Canadian grant for development of peptide-based drug delivery vehicle
Asep gets Canadian grant for development of peptide-based drug delivery vehicle
June 26, 2023 -- Asep Medical announced Friday that it has been awarded a grant by the NanoMedicines Innovation Network (NMIN) to develop a nanoparticle-formulated peptide solution as a drug delivery vehicle for treating chronic sinus infections caused by biofilms. Read More
 Scanning ion conductance spectroscopy in study enables precise DNA identification
Scanning ion conductance spectroscopy in study enables precise DNA identification
June 21, 2023 -- Researchers at the Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) have developed a new nanopore approach for manipulating individual molecules such as DNA that allows unprecedented control and precision. Read More
 Reveal Genomics highlights results for breast cancer predictive test in phase II clinical trial
Reveal Genomics highlights results for breast cancer predictive test in phase II clinical trial
June 15, 2023 -- Precision oncology firm Reveal Genomics on Thursday announced that its HER2Dx genomic test for HER2+ breast cancer has been validated in the PHERGain phase II clinical trial. Read More
 Eli Lilly acquiring immune therapy developer Dice Therapeutics for $2.4B
Eli Lilly acquiring immune therapy developer Dice Therapeutics for $2.4B
June 22, 2023 -- Eli Lilly said this week it has inked an agreement to acquire Dice Therapeutics, a biopharma firm developing novel oral therapeutic candidates, for $2.4 billion in cash. Read More
 Chikungunya vaccine candidate in clinical trial found generally safe and effective
Chikungunya vaccine candidate in clinical trial found generally safe and effective
June 13, 2023 -- A study of U.S. adults found that a vaccine candidate for chikungunya disease was generally safe and well tolerated. Read More
 Biotech firm AltPep closes $53M Series B financing round
Biotech firm AltPep closes $53M Series B financing round
June 23, 2023 -- AltPep, a biotech firm developing early detection tests and disease-modifying treatments for amyloid diseases, on Friday announced the closing of a $52.9 million Series B financing round. Read More
 Sound waves test protein-protein bond strength
Sound waves test protein-protein bond strength
June 9, 2023 -- Temporary protein-protein bonds are essential for many bodily functions, including enzymatic reactions, antibody binding, and responses to medication. Read More
 Scientists create cell atlas of developing human lung
Scientists create cell atlas of developing human lung
December 9, 2022 -- Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, EMBL’s European Bioinformatics Institute, the Gordone Institute at the University of Cambridge, and collaborators have created a spatiotemporal cell atlas of the developing human lung. From the mapping, they have identified 144 cell states in the early stages of life and their interactions in new detail. Read More
 Senescent neuron discovery in brains opens path for Alzheimer's drug development
Senescent neuron discovery in brains opens path for Alzheimer's drug development
December 2, 2022 -- Scientists at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies have found that neurons from people with Alzheimer's disease show deterioration and undergo a late-life stress process called cellular senescence, while senescent cells could be a way to slow neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Read More

Science In Brief
Conferences
Connect
Latest Tweets